|
Supplement to Stratified Regression Chapter
Presentations
None
Assignment
Question 1: Estimate
mortality rate in 6 months for lung cancer patients with various common
comorbidities. Data► SQL► Jehanzeb's
Solution► Video►
- Use
SQL to construct case/control comparisons for each comorbidity of
lung cancer.
- Use
SQL to estimate the intercept for parameters of the multiplicative
function form.
-
Report the mortality rate for patients who just have lung cancer and
no other comorbidities.
-
Provide the equation that calculates the risk for combination of
lung cancer and its comorbidities.
-
Select 3 comorbidities and calculate the prognosis of a patient with
a combination of 3 comorbidities and lung cancer.
Question 2: Many patients, at end of life, experience
disabilities. In fact, disabilities are often used to anticipate end of
life. The attached data show the disabilities residents of veteran
administration nursing homes have experienced. Estimate how
various disabilities predict mortality in 6 months. The data do
not have headers. The variables are listed in the following order:
ID, age, gender (M for male, F for Female), number of assessments
completed on the person, number of days followed, days since first
assessment, days to last assessment, unable to eat, unable to transfer,
unable to groom, unable to toilet, unable to bathe, unable to walk,
unable to dress, unable to bowel, unable to urine, dead (1) or alive
(0), and assessment number. The following table should assist in
organizing the data.
|
ID |
Age |
Sex |
tAssess |
Followed |
DaysFirst |
DaysLast |
uEat |
uSit |
uGroom |
uToilet |
uBathe |
uWalk |
uDress |
uBowel |
uUrine |
Alive |
AssessID |
|
1 |
66 |
M |
9 |
915 |
0 |
915 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
66 |
M |
9 |
915 |
7 |
908 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
1 |
66 |
M |
9 |
915 |
18 |
897 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
|
1 |
66 |
M |
9 |
915 |
238 |
677 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
-
Clean the data using the following steps: The age at death is given
as a row of data. For each assessment calcualte if the patient dies
in 6 months from the assessment. If the patient never dies assume
not dead in 6 months. At death assume that the patient has all
disabilities, as is the data indicates no disabilities at death.
Drop last assessment as no outcomes can be calculated from last
assessment. Assume age of assessment is age at first assessment
(given as the second variable) plus days to assessment/365.
Residents with negative age should be dropped because of date of
birth errors. Residents 100 or more years should be dropped because
of small sample. Note that the analysis is done at assessment level
and not at patient level. Data► Clean►
-
Predict from the patient's assessments (i.e. their age, gender, and
disabilities at time of assessment) if the patient is likely to die
in the next 6 months and may be a candidate for hospice care. Do
not use regression in these analysis and estimate the parameters
using SQL. SQL► Answer►
-
Calculate the k constant for the multiplicative model using SQL. SQL►
Generate possible k values and see which one of the k values satisfy
the equation:
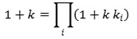
- Use
the model you have developed to predict the probability of mortality
for a 75 year old resident with urine, bowel, and toilet
disabilities. Enter the case description into a table called
RecentCases, using Create Table and Insert Value commands. Then use
this table to predict the probability of mortality for this
resident. SQL►
Make sure that the probability of mortality is adjusted to range
between minimum amd maximum probabilities for different strata.
Stratfied regression provides a transformed probability that should
be adjusted to estimate the actual probability using this formula:

Where Max is the maximum and Min is the minimum probabilities for
each strata.
More
For additional information (not part of the required reading), please
see the following links:
-
Multi-attribute preference functions. Health Utilities Index. PubMed►
-
Utility functions for health profiles PubMed►
- How
decisions reveal our preferences PubMed►
|
![]()