HAP 786: Workshop in Health InformaticsLecture: Create Database in All of Us
Overview
Objectives
Assigned Reading & Learning MaterialsDifferent student teams have different assignments and thus you should not follow the code of others verbatim. Please note the following videos are organized to serve a specific type of regression and the variables you need in your database could be different. For missing value or miss-match between language and machine learning models, you need to work with the entire cohort. You need to think through what are the dependent and the independent variables. These would be different in different projects. For missing value or miss-match project the dependent variable is a condition in All of Us and the independent variables are other conditions, medications, or factors. For other projects, your dependent variable could be response to antidepressant or a predictor of response to antidepressant. In creating the database, you need to make sure that all independent variables occur prior to the dependent variable.
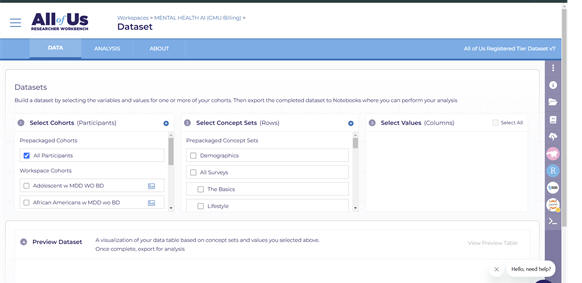
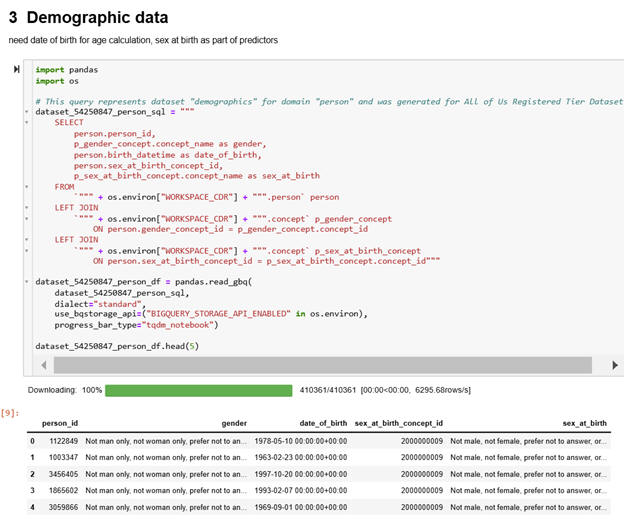
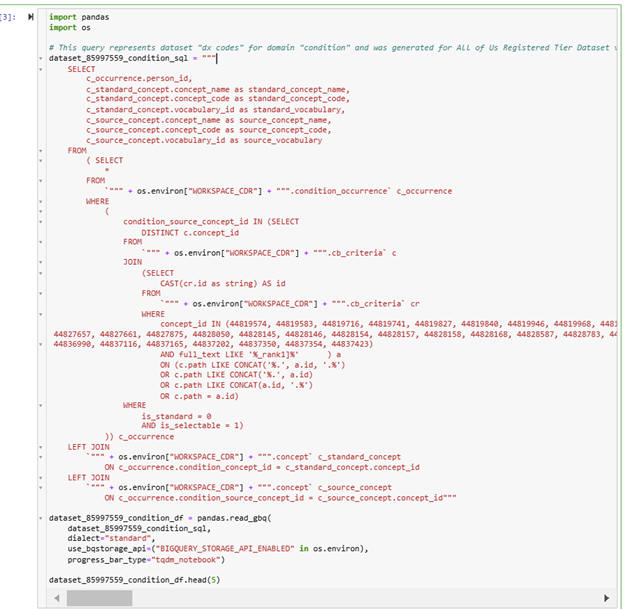
AssignmentIn this session, you are asked to organize the database for your analysis. Analysis of observational data requires that you pay attention to timing of variables. In organizing your database, it is important to make sure that you include timing of the variables. You need to (a) create a cohort, (b) create a database, and (c) add specific variables missing in the database. Create Cohort and Related Data Sets for the Missing Value Project. You are tasked with organizing a database for analysis of missing values in predicting response to antidepressants. Observational data analysis requires careful attention to timing. In structuring the database, include timing variables and complete the following:
|